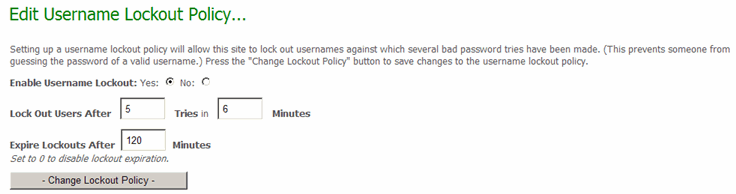
Setting up a username lockout policy will allow this site to lock out usernames against which several bad password tries have been made. (This prevents someone from guessing the password of a valid username.) Once User Lockouts have been enabled and configured, a user who attempts to sign on with an incorrect password will be locked out following a specific number of failed attempts in a certain amount of time. Lockouts can also be set to expire after a configurable amount of time has elapsed.

MOVEit supports the following authentication methods:

Please also note that "change password on next signon" checks will NOT be enforced in any mode other than "MOVEit DMZ".
Authentication Sources
When the organization's Auth Method is set to EXTERNAL Then MOVEit, or EXTERNAL Only, the Authentication Source list becomes available. Here, an administrator may add, edit, remove, and change the priority of the external authentication sources configured for this organization. When a user signs on to the organization for the first time, each active authentication source will be tried, in the order they are listed here. If a user successfully authenticates to one of the sources, that source is recorded in the user's profile, so that they will be immediately authenticated against it the next time they sign on (see the Authentication Source Affinity section of the User Profile page for more details).
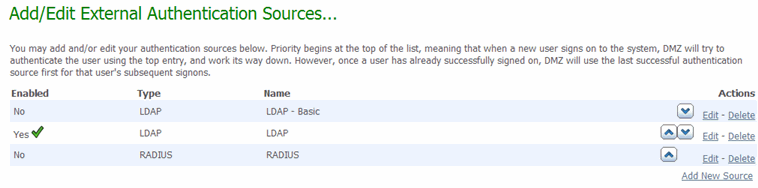
The up and down arrows in the Actions column allow you to change the order in which the authentication sources are queried.
For more information about adding and configuring external authentication sources, see the External Authentication documentation in this section.
This section allows an administrator to edit the default Deny Multiple Signons setting for the organization. New users will be created with the default setting, and when changed, an option is provided to set all current users with the new setting value. When Deny Multiple Signons is enabled, users will not be allowed to signon to the system using the same interface from different IP addresses. For example, a user WILL be allowed to sign on to the web interface from one machine, and the FTP interface from another, but will NOT be allowed to sign on to the web interface from two different machines.
This section is where administrators may list, add, edit, delete, and assign Expiration Policies. These policies govern how accounts that are assigned the policy will be considered expired and removed from the system. For more information about creating and assigning expiration policies, see the Expiration Policies Feature Focus page.