You should consider using Windows Server's IIS SMTP server as a local mail relay on your MOVEit DMZ system any of the following conditions apply.
MOVEit DMZ sends out new file notifications and upload confirmations immediately after saving the related file to disk. While this approach affords near real time response, it also forces MOVEit DMZ to wait for each message to be sent before another can be attempted. When MOVEit DMZ is dealing with busy mail servers or a lot of recipients, the upload process will spend more time sending email than saving files. To keep MOVEit DMZ from having to wait up to 10 seconds for each message to be sent, we can instead spool these messages to the local SMTP server, which will then spool these mail messages out to "real" email servers when they are better able to accept the traffic.
If a local mail relay server is configured, DMZ can use this to queue up outgoing mail instead of going directly to the main mail server. This frees DMZ up to move on to other tasks, and can provide a noticeable improvement in responsiveness for most file transfer operations.
Windows Server 2008 - For Windows Server 2008 you will need to install the SMTP Server and the IIS 6 Management Console Role Service. Using the Server Manager from Administrative Tools, enable the "SMTP Server" feature. Then enable the IIS 6 Management Console Role by going to Roles -> Add Role Services -> IIS 6 Management Console. Then click "Install". Once you have these two items enabled you may proceed to the following sections.
Ensure that you have the SMTP component installed in your local IIS server. When installed correctly, you should see a Default SMTP Virtual Server node in your IIS administration window under the local machine. If you do not have the SMTP component installed, you will need to install it through the Add/Remove Windows Components option of the Add/Remove Programs window, which can be found in the Control Panel.

Open up the properties window of the SMTP service by right-clicking on the SMTP service node and selecting Properties. In the properties window, select the Access tab. In the Access tab, open the Connection Control window by clicking on the Connection button in the Connection Control section. Restrict access to the SMTP server by selecting the Only The List Below option and adding the localhost IP address 127.0.0.1 to the access list. Click OK to exit the window.
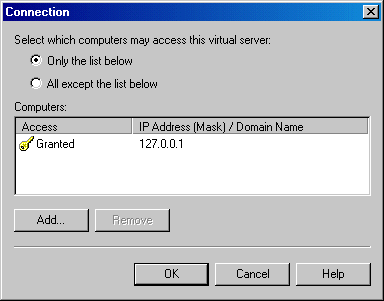
In the Access tab, open the Relay Restrictions window by clicking the Relay button in the Relay Restrictions section. Restrict relay access to the SMTP server by selecting the Only The List Below option and adding the localhost IP address 127.0.0.1 to the access list. Make sure the Successful Authentication Relay option is turned off. Click OK to exit the window.
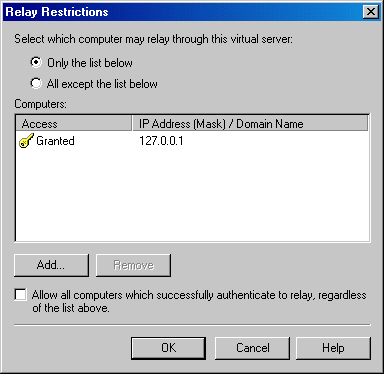
In the Properties window, switch to the Messages tab. In the Messages tab, turn off all the message limits.
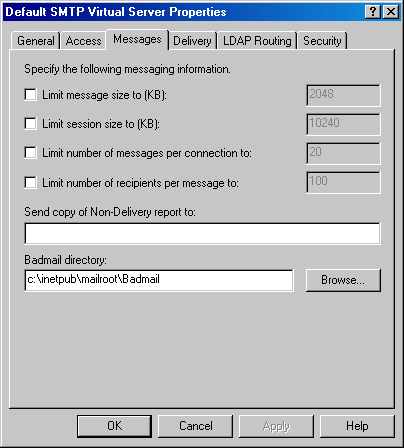
In the Properties window, switch to the Delivery tab. In the Delivery tab, change the default delivery intervals and timeouts to smaller values. Recommended values are shown in the image below.
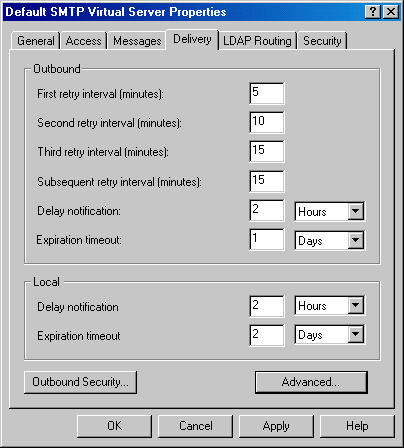
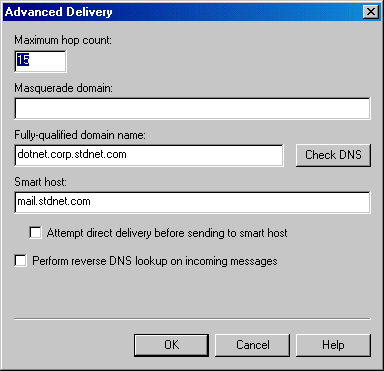
In the Delivery tab, open the Advanced Delivery Options window by clicking the Advanced button. Set the Fully Qualified Domain Name setting to the name of your MOVEit DMZ server. Set the Smart Host setting to the name of your main SMTP server. Click OK to exit the window. Configuration of the SMTP server is now complete. Click OK in the Properties window and make sure the SMTP service is started.
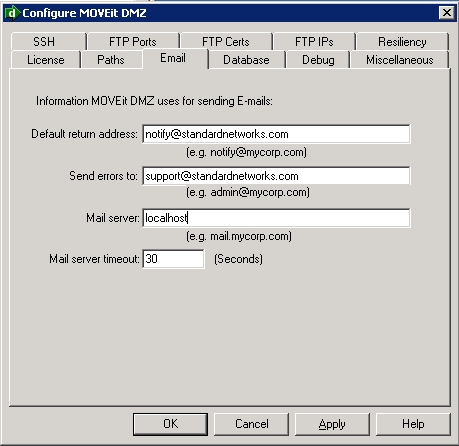
The final step is configuring your DMZ server to use the new local SMTP service. Open the MOVEit DMZ Config program (Start -> Programs -> MOVEit DMZ) and switch to the Email tab. Enter localhost as the Email Server Name. Click OK to exit the Config program. The change should happen immediately; no restart is required.
You will probably want to tinker with the "outgoing connection limit" (default is 1000) if one of your goals is to keep MOVEit DMZ from overloading your "real" mail server. (Typical "throttled" values are from 1-5.) To alter this setting, open the SMTP properties, go to the "General" tab and open the "connection" dialog.
Your local SMTP relay server should now be set up, and your MOVEit DMZ server configured to use it.
If you are running MOVEit DMZ Resiliency, you must repeat this procedure on every node in the cluster (even application nodes.)
An easy way to troubleshoot your mail relay loop is to run the "reporterrors.exe" executable found in your "\MOVEitDMZ\Scheduler" folder from the command line. This utility will either send a very short message to the "error email address" configured in your MOVEit DMZ Config program or report a connection problem regarding the email server.
Problem: Cannot connect to local mail relay.
Solution 1: Open the "Services" from "Start | Programs | Administrative Tools". Make sure the "Simple Mail Transport Protocol" service is started and that it is set up to start "Automatically."
Solution 2: Open the "Internet Services Manager" from "Start | Programs | Administrative Tools". Make sure the "Default SMTP Virtual Server" is NOT "stopped".
Solution 3: Open the "Internet Services Manager" from "Start | Programs | Administrative Tools". Right-click on "Default SMTP Virtual Server" and select Properties. In the General tab make sure the IP Address is set for "All Unassigned".
Solution 4: Go to the command line and type "netstat -a -n". Look for any TCP entries with a local address ENDING with ":25". If there are none, the SMTP server failed to bind to its listening port; reboot the server.
If the "reporterrors.exe" utility reports that it is sending email OK, but the mail messages are not actually reaching their destination, open the local SMTP server queue folder and look for messages there which correspond with your test messages. (The queue folder is usually named something like "c:\inetpub\mailroot\queue".)
Problem: Mail is being queued on the local SMTP server and is not being delivered.
Solution 1: Make sure your SMART HOST contains the value which used to be the MAIL SERVER field in your MOVEit DMZ configuration.
Solution 2: Make sure the "Attempt Direct Delivery" box (near the Smart Host setting) is NOT CHECKED.
Solution 3: Look for entries in your SYSTEM event log from SMTP or SMTPSVC which complain about "DNS" problem. If you see events like these, change the SMART HOST (described above) to an IP address surrounded by square brackets. (e.g. "[66.170.5.142]")
You can also use the "MOVEit DMZ Check" utility to test mail relay loops. In version 4.0 it acquired the ability to test email relay against an email address you type in while the program is running, so it may be the better tool to use if you suspect trouble with particular email addresses.