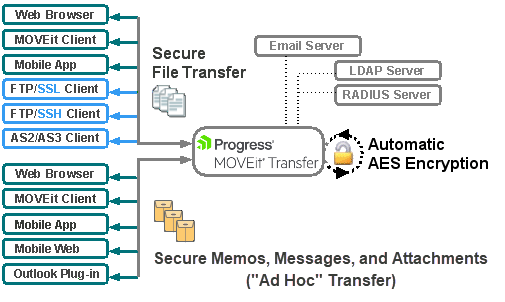
Web browsers and no cost/low cost secure FTP clients can quickly, easily, and securely exchange files with MOVEit Transfer over encrypted connections using the HTTP over SSL (https), FTP over SSL (ftps) and FTP over SSH (sftp) protocols. And all files received by MOVEit Transfer are securely stored using FIPS 140-2 validated AES encryption, the U.S. Federal and Canadian government encryption standard.
MOVEit Transfer includes a web interface for online administration and monitoring of MOVEit activities, and a programmable interface (via MOVEit API Windows and MOVEit API Java) to make it accessible to custom applications.
MOVEit Transfer includes an optional MOVEit Wizard plug-in for web-based users to quickly upload and download large and/or multiple files and folder trees to and from MOVEit. A Microsoft Outlook and Microsoft 365 add-in is available for Ad Hoc Transfer.
User and Client Applications that Use MOVEit Transfer
Encryption capabilities throughout the MOVEit product line are provided by MOVEit Crypto, a compact and fast dynamically-linked library. The AES encryption in MOVEit Crypto has been FIPS 197 validated. The entire cryptographic module has been FIPS 140-2 validated after rigorous examination by cryptographic specialists in the United States' National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and Canada's Communications Security Establishment (CSE).
Validation of AES Encryption Standards

MOVEit also has an approved Certificate of Networthiness (CoN) from the United States Army. This certification involves a review of how MOVEit meets Army requirements for network security, integration, interoperability, and ease of management and support.
The MOVEit software itself resides on a Microsoft Windows Server platform hardened against threats from the Internet and trusted networks. Organizations that need to support very large volumes of file transfers and/or many users may require additional hardware, but for many organizations the minimum recommended specifications are okay.
For a complete list of hardware, software, and database requirements, see the MOVEit Transfer Release Notes.
In a typical network topology MOVEit is best located on a secured DMZ segment accessible to both internal and external users. DMZ is short for Demilitarized Zone - a network area where both internal and internet hosts are allowed to connect. By default, connections originating from a DMZ network segment are not to be trusted and are usually not allowed unless there is a compelling case to allow a particular service through. The following visual demonstrates end-user and client Applications that Use MOVEit Transfer.
Example Deployment Pattern (MOVEit Gateway, web farm, and High-Availability pattern not shown)
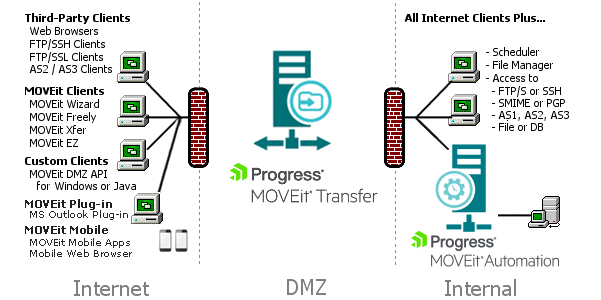
Web and secure FTP clients can upload and download files to the MOVEit server from internal and external networks. For security reasons, MOVEit Transfer is NOT permitted to establish connections with or push files to systems on either your internal network or on an external network. (If a "proxy push" or "proxy store-and-forward" solution is desired, MOVEit Automation can be used with MOVEit Transfer to fill this role.)
There are three areas where files are at risk when transferred between an external network (such as the Internet) and your internal network:
Most secure Web and FTP file transfer products reside on a system in a DMZ and use industry-standard SSL or SSH to provide secure transfers between the Internet and DMZ. (MOVEit Transfer provides this level of security and functionality as well.) Unfortunately, that is as far as most products go; they fail to secure files stored on the DMZ (at risk if the DMZ box gets hacked) and fail to secure files being transferred between DMZ and MY ORG (at risk if a hacker sets up a sniffer inside the DMZ).
MOVEit Transfer secures all three areas by using SSL/SSH-encrypted transfers for ALL transfers and by using FIPS 140-2 validated AES encryption to secure files on disk.
In addition, only MOVEit offers complete end-to-end file integrity over FTP. In other words, files transferred with secure FTP or web clients which support file integrity checks through the MOVEit system can be proven to be 100% identical to their source files through the use of SHA-1 cryptographic hashes. (When combined with authentication, complete file integrity provides non-repudiation.)