Using the Web Task Manager - Process tab
The Processes tab provides key indicator process information for a selected device that WhatsUp Gold is monitoring. This information helps you learn about device processes and identify trends and issues that occur on a particular network device. You can use the Web Task Manager to view the processes running on WMI- or SNMP-enabled network devices.
Note: Microsoft Windows Server 2003 reports the VM Size column information in Kilobytes instead of Bytes. This is a known issue to be corrected in a future WhatsUp Gold release.
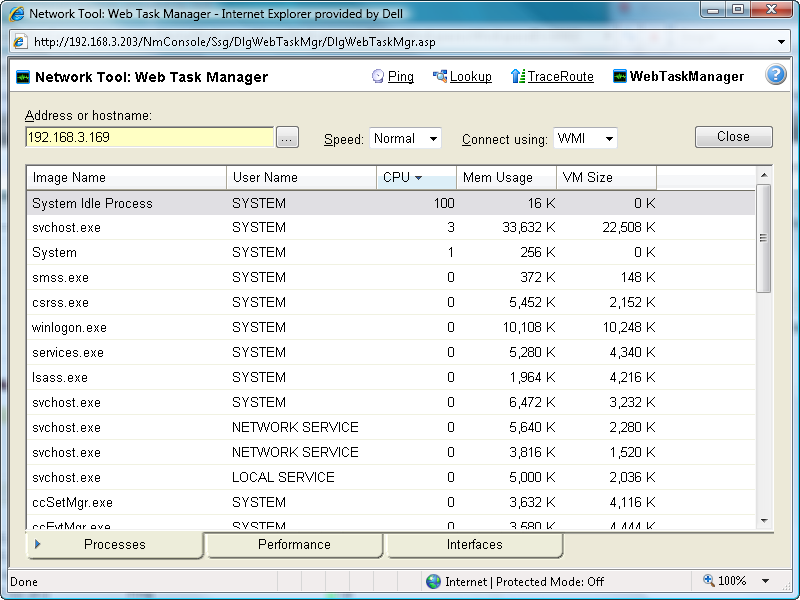
After you have identified a process that is causing device performance issues, such as an application executable like Outlook.exe running multiple instances of the program, you can correct the problem to bring the device performance back to normal.
Note: Unlike the Windows Task Manager, you cannot terminate processes using the Web Task Manager. To terminate a task, you must log in to the computer where the task is running and use the Windows Task Manager to end the process.
To use the Web Task Manager:
- Open the Web Task Manager.
- From the web interface, click GO. The GO menu appears.
- If the WhatsUp section is not visible, click WhatsUp. The WhatsUp section of the GO menu appears.
- Select Tools > Web Task Manager. The Web Task Manager appears.
- Enter or select the appropriate information for the following fields:
- Address or hostname. Enter a device IP address to select a device for which you want to view process information. Click Reconnect to connect with a device that has disconnected from the Web Task Manager.
- Browse (...). Click to open the Web Task Manager Credentials dialog and set a WMI user name and password or an SNMP read community. The credential options are provided from the credentials stored in the Credentials Library.
- Speed. Select the speed at which you want to monitor the device performance.
- Normal. Updates device information every one second.
- Medium. Updates device information every five seconds.
- Slow. Updates device information every ten seconds.
- Paused. Stops updating device information.
- Connect using. Select the device protocol (WMI or SNMP) used to monitor and manage the device. The credentials stored in the Credentials Library are used to connect and read information on the selected device.
Note: When viewing information for devices running Microsoft Windows, information gathered by SNMP may reflect a delay of one minute or more. This delay is caused by a limitation in how often Microsoft Windows updates SNMP values. For this reason, we recommend using a Speed of Medium or Slow when using SNMP to view interface information about a device running Microsoft Windows.
- At the bottom of the Task Manager page, select the tab that you want to use (Processes, Performance, or Interfaces).
- For troubleshooting information, see Troubleshooting SNMP and WMI connections.
Note: Some differences exist in column names between the Web Task Manager and Windows Task Manager in Windows Vista and Windows 2008. The Mem Usage column in Web Task Manager is named Working Set (Memory) in Windows Task Manager on Windows Vista and Windows 2008. The VM Size column in Web Task Manager has no corresponding column in Windows Task Manager on Windows Vista and Windows 2008.