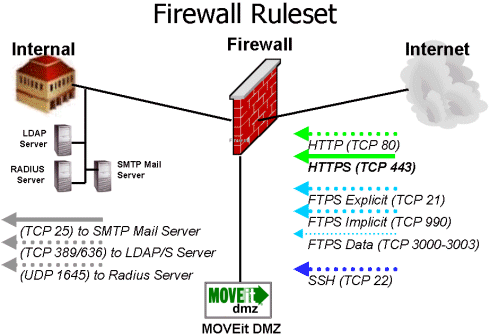
MOVEit DMZ was designed first and foremost to be secure on production "DMZ" segments exposed to the Internet. Like any well-behaved DMZ resident, MOVEit DMZ should "speak only when spoken to," and then only over ports MOVEit DMZ controls. You can enforce this behavior on your firewall using two very restrictive deny rules and a handful of permitted access rules.
The world normally uses HTTPS, FTP over SSL (FTP/SSL, ftps) and/or FTP over SSH (FTP/SSH, sftp) to communicate with MOVEit DMZ. MOVEit DMZ also normally needs to access the SMTP services of another mail server to deliver notification messages.
Nonsecure HTTP services are optional and generally not recommended. If nonsecure services ARE enabled, MOVEit will simply redirect users to the secure services. (IIS by itself doesn't redirect.) As suggested by the diagram below, access to different services from different locations (i.e. "Internal" vs. "Internet") can also be controlled by the firewall.

To prevent outside forces from opening unauthorized connections to MOVEit DMZ, use the following rule:
To prevent MOVEit DMZ from opening unauthorized connections to outside computers, use the following rule.
Now, depending on which services you elect to run on MOVEit DMZ, you will need to open a few ports. The criteria and specifics are covered below.
MOVEit DMZ normally listens for NONSECURE web connections on TCP port 80 and SECURE web connections on TCP port 443. Remote users NEED to be able to connect to the secure port (443) from remote addresses. Optionally, you may leave port 80 open as well if you would like MOVEit DMZ to "be friendly" and auto-redirect users connecting on the nonsecure port to the secure port instead.
If MOVEit DMZ FTP needs to support clients over the Internet, Ipswitch strongly recommends you REQUIRE PASSIVE MODE FTP TRANSFERS and LOCK PASSIVE DATA PORTS TO A SMALL RANGE on MOVEit DMZ FTP.
WARNING: Simply specifying "FTP" on your firewall will rarely be enough to allow secure FTP through (unless both client and server use the "CCC" option). Firewalls that "understand FTP" look for the phrase "PORT" in data channels and open temporary holes in the firewall for communications over the designated ports between the two machines on either side of the data channel. However, secure data channels are encrypted, meaning the firewall will be unable to open any temporary ports.
Explicit FTPS control connections take place on TCP port 21.
Implicit FTPS control connections take place on TCP port 990.
If you use FTPS on your MOVEit DMZ, it is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that you configure it to use both explicit and implicit modes (for greatest client compatibility), passive mode (to allow the server to select port numbers) and to use a restricted range of ports (to avoid opening up a hole which a trojan horse could use).
"CCC" Command - Alternative to Range of High Open Ports
As of version 3.2, MOVEit DMZ supports the "CCC" FTP command. The "CCC" command was invented to allow FTP-aware firewalls to understand the "PORT" commands otherwise hidden by FTP over SSL. Specifically, the CCC command allows the "PORT" commands to be understood by firewalls by dropping the control channel (and only the control channel) out of encrypted mode and into cleartext mode.
Although it provides greater flexibility, there are two security risks involved when using the CCC command. The first is that someone could sniff the now cleartext port command to connect to the secure FTP server and either steal data by connecting as if they were the real client or cause a denial of service attack by preventing the real client from connecting. The second is that someone can sniff foldernames, filenames and custom commands such as "change password" while the control channel is unencrypted. (The security risk of the alternate solution - a limited number of open ports - is that another service could be installed on that server and could start listening on those ports.)
Active FTP - Not Recommended
(Active FTP is NOT recommended for Internet connections because remote firewalls will likely not permit active FTP data connections in, especially if they are encrypted!)
Passive FTP (Unrestricted) - Not Recommended
(Setting Passive FTP up in "unrestricted mode" is not recommended because proper operation of this mode requires a wide range of high ports (thousands) to be open on the firewall.)
MOVEit DMZ normally listens for SECURE FTP "control" connections on TCP port 21 (and 990 when using implicit mode). As a "passive" FTP server, MOVEit DMZ will then listen for a SECURE FTP "data" connection on the TCP "high port" (>1023) it negotiated with the client. These ports need to be left open for proper communication.
Passive FTP (Restricted) - Recommended
MOVEit DMZ normally listens for SECURE FTP "control" connections on TCP port 21 (and 990 when using implicit mode). In "restricted passive mode" MOVEit DMZ listens for SECURE FTP "data" connections on a configurable finite range of contiguous TCP "high ports" (e.g. "3000,3001,3002,3003") that it specifies to a particular client. (Nothing extra needs to be configured on clients other than to specify "passive" mode transfers.) These ports need to be left open for proper communication.
Additional Ports for Client Certificates
If you require that all your FTP/SSL traffic authenticate with client certificates there is no need to set up additional FTP/SSL ports for this purpose. However, if you wish to require some FTP/SSL connections/users authenticate with client certificates while others do not face this requirement (common during migrations), you will need to set up additional ports for FTP/SSL client certificate authentication.
Client certificate authenticated sessions use the same data ports as "regular" FTP/SSL sessions, so no additional data ports are needed. However, a second Explicit control port and a second Implicit control port are typically assigned to a MOVEit DMZ FTP server in this situation. For example, Ipswitch uses ports 21 and 990 to handle its non-client-cert-authenticated connections and ports 10021 and 10990 to handle its client-cert-authenticated connections.
MOVEit DMZ uses a one-port SSH tunnel to support FTP over SSH clients. The use of a single SSH tunnel has an advantage over the multiple encrypted data streams used by FTP over SSL: fewer ports need to be opened on a firewall. (FTP over SSH is a "single port" secure transfer protocol.) The one port normally used by SSH is TCP port 22.
The MOVEit DMZ server requires the use of an SMTP-compliant mail server to send email notifications. If your MOVEit DMZ server must pass through a firewall to reach a mail server, you should allow MOVEit DMZ access to it only over TCP port 25. If you would like the ability to queue messages if your mail server is unreliable, need special authentication parameters to relay mail, or generally plan on sending many notifications at once, please consider setting up the local mail relay. NOTE: The MOVEit DMZ server need not access an internal email server if you can point it to your "upstream" (ISP) mail relay instead.
If you intend to use RADIUS remote authentication, MOVEit DMZ must be able to communication via UDP to the remote RADIUS server. The UDP port normally used to support RADIUS is 1645, but this port is configurable (like most other ports in MOVEit DMZ).
If you intend to use LDAP remote authentication, MOVEit DMZ must be able to communication via TCP to the remote LDAP server. The TCP port normally used to support LDAP is 389 and the port normally used to support LDAP over SSL is 636, but these ports are configurable. (The use of LDAP over SSL is strongly recommended; most modern LDAP servers support this. For example, see the "Active Directory - SSL" section of the "Feature Focus - External Authentication" documentation for instructions to enable SSL access on Active Directory LDAP servers.)
If MOVEit DMZ will connect to a remote Microsoft SQL Server database, such as in a web farm, the MOVEit DMZ node must be able to communicate over the SQL Server ports. Port 1433 is the default SQL Server port, if you have configured a different port for your SQL Server instance, use that port instead of 1433. You need to open port 1434 only if you plan on running SQL Server Studio or another SQL Server utility on the MOVEit DMZ application nodes themselves.
If MOVEit DMZ Resiliency is in use, each node and the NAS must allow Microsoft networking protocols between them. This is normally accomplished by opening TCP port 445 between the various machines. However, this port should NOT be left open to or from the Internet.
If MOVEit DMZ Web Farms is in use, each node and the NAS must allow Microsoft networking protocols between them. This is normally accomplished by opening TCP port 445 between the various machines. However, this port should NOT be left open to or from the Internet.
Some sites, especially those regulated by the FDA and those using MOVEit DMZ Resiliency, may need to ensure that the clock on MOVEit DMZ is kept in sync with a known, external source. The hostnames of good external time sources such as "time.nist.gov" can be found on various lists of public time servers.
Time services (RFC 958) normally use UDP port 123. When setting up firewall rules to support external time service, you must allow UDP packets to travel from any high port on the MOVEit DMZ to remote UDP port 123, hopefully on one or a small collection of remote servers. Return traffic using the same UDP port must also be able to return to your MOVEit DMZ server.
Please note that your firewall itself MAY also be able to act as a time server, in which case the firewall queries external time servers itself instead of permitting every machine behind the firewall to get its own time.
Also note that servers that are members of a domain are automatically time synchronized with the domain controller, so no external time server is necessary.
If you elect to send MOVEit DMZ Audit Events to a SysLog server, you will likely need to allow UDP SysLog packets to travel from your MOVEit DMZ to the SysLog server on UDP port 514.
If you elect to send MOVEit DMZ Audit Events to a SNMP management console, you will likely need to allow UDP SNMP packets to travel from your MOVEit DMZ to the SNMP management console on UDP port 161.
This procedure has largely been replaced by MOVEit DMZ API's ability to run ad-hoc custom reports against most MOVEit DMZ configuration elements and audit entries remotely over a secure connection.
If you elect to set up an ODBC stunnel connection (as described in "Advanced Topics - Database - Remote Access"), you will likely need to allow connections from MOVEit Central to MOVEit DMZ on TCP port 33062. This port is configurable and may be changed in both the "stunnel_mysqlserver.conf" and "stunnel_mysqlclient.conf" configuration files involved.
MOVEit Freely and MOVEit Buddy are secure FTP clients. See the "Remote Secure FTP Over SSL Clients section" above for required port information
MOVEit Central normally communicates with MOVEit DMZ via HTTPS. See the "Remote Web Browser (HTTP/S) section" above for required port information.
The MOVEit Wizard, MOVEit Xfer, MOVEit DMZ API and MOVEit EZ clients all communicate with MOVEit DMZ via HTTPS. See the "Remote Web Browser (HTTP/S) section" above for required port information.
AS2 clients normally use HTTPS. In rare cases they may use HTTP instead. See the "Remote Web Browser (HTTP/S) section" above for required port information.
AS3 clients are secure FTP clients. See the "Remote Secure FTP Over SSL Clients section" above for required port information