You can tag traffic on your network to make it easier to manage, associate with specific services or applications, and recognize in NOC dashboards and detailed reports by using the NTA Applications Library. You can also tag traffic for cases where the same port is in use by two different services or when different service instances of the same application run over separate network segments or subnets.
Tip: After you apply these tags, you can check if your sources have observed traffic that matches these rules by checking the Top n Applications or Top n Conversations reports. Conversely, these application mappings will remove items from the Unclassified Traffic report.
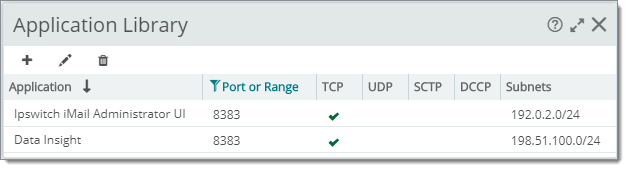
Defining Application Library Rules for two Services Using Port 8383 (viewed with port filter set to "8383")
NTA Applications enable you to tag network traffic based on:
Use Mappings Defined in the NTA Application Library
NTA Applications Library already comes fully prepopulated with the more common application-to-port and transport protocol associations, many of which are the more common applications described in the IETF's well-known port definitions (a list of companies that applied with the IETF standards body with a specific port number).
Use Custom Mappings
If you want to provide a more specific label than would be associated by using the default NTA Applications associations, you can also override these on an entire-network or subnet-by-subnet basis or redefine them for different transport protocols (UDP versus TCP, for example).
Important: Any time you specify a port association (NTA Application) with a Subnet, NTA will override any global scope cases (an association where you did not specify a Subnet) for data within the subnet range specified.
To add a port mapping:
|
Specifying an Application for a Specific Subnet (port for iMail WebUI shown)
|
When overriding or applying more specific application labeling for a well-known port/application association, it is best practice to do this in the NTA Applications Library at the lowest scope necessary (subnet level) and then document this change as part of your network operations.
Subnet Specified |
Port Specified |
Behavior |
192.0.2.0/24 |
8383 (iMail Admin UI) |
Only traffic seen within a specific subnet will be labeled with Ipswitch iMail Admin UI application within NTA reports and dashboards. Other traffic outside this subnet range and outside other well-known port associations will be considered Unclassified. Note: If you do not specify a subnet the NTA Application port association becomes global. In other words, it is applied to all NTA traffic. |
Subnet Specified |
Port Specified |
Behavior |
None |
8383 (Ipswitch iMail admin) |
All flow traffic detected will be labeled with Ipswitch iMail Admin application in NTA reports and dashboards. Note: If you do not specify a port, the NTA Application port association becomes global. In other words, it is applied to all NTA traffic. |
Note: Network Traffic Analysis considers network traffic to be "unclassified" when both source and destination ports are either outside the well-known port range or not classified in the Application Library.
Tip: Leverage general NTA application rules (port 8383 = TCP, for example) for large network segments. Then add specific rules for the same port and tune port identifications for certain subnets where it makes sense (for example for a smaller network segment, Port = 8383 on Subnet = 192.0.2.0/24 could be tagged as Ipswitch iMail).