|
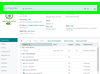
 Device Configuration. Control how your device is monitored, managed, and represented within WhatsUp Gold. (Includes roles determination as well as network and hardware information used to identify monitor selection and device boundaries). Device Configuration. Control how your device is monitored, managed, and represented within WhatsUp Gold. (Includes roles determination as well as network and hardware information used to identify monitor selection and device boundaries).
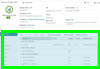
 Monitors. Browse, apply, and configure passive, active, and performance monitors to this device. Monitors. Browse, apply, and configure passive, active, and performance monitors to this device.
- Active. Check availability, simulate user or exercise services or APIs, and return up or down indicator.
- Passive. Check for specific logged or trapped event.
- Performance. Measure performance statistics and trigger alerts and actions based on thresholds.
: The grid on the Monitors tab is filtered by default to only show monitors assigned to the device that are currently enabled. To display all assigned monitors, hover your cursor over the Enabled column header, click the drop-down arrow that appears, then clear the applied filter from the options displayed.
: You now have the ability to specify the protocol by which WhatsUp Gold collects CPU, Disk, Memory, and Interface utilization data from the device. From the Monitors tab, select the applicable monitor, click  , then select the desired protocol for collecting performance data at the top of the configuration dialog. , then select the desired protocol for collecting performance data at the top of the configuration dialog.
Learn More
: In WhatsUp Gold, a given device is considered to be in a down state if it has either a critical monitor down or all monitors down.
 Polling. Adjust polling interval, target address, and dependency chain. Polling. Adjust polling interval, target address, and dependency chain.
- . Determines how frequently WhatsUp Gold fetches observations from this device.
- . Select an IP address for a particular interface or resolve to a specific DNS hostname.
- . Drop the managed device to maintenance mode and specify a date and time for the maintenance period to end without further end-user interaction, if desired. (Useful mode and marker in reports and for SLA accounting.)
- []. Poll based on the status of another device or resolved host.
: If you need to apply a shorter poller interval either temporarily, or for troubleshooting performance, consider using the RealTime Performance monitor.
: In WhatsUp Gold, a given device is considered to be in a down state if it has either a critical monitor down or all monitors down
- . Specify when the selected device regularly enters/exits maintenance mode without user interaction.
 Actions. Send notifications, log events, chain together corrective actions and apply escalation rules. Actions. Send notifications, log events, chain together corrective actions and apply escalation rules.
When you apply active monitors, you typically associate an action and a device state with changes observed by the monitor. There are three main categories of built-in action types available through the Actions Library. Actions can be triggered or scheduled.
: Certain actions (CM Actions, for example) can be invoked on demand ().
Built-in action types include:
- Notifications. Send messages to stakeholders and responsible individuals according to site policy.
- Remote execution. Create scripts, execute remote programs, and apply configuration changes.
- Log. Include state change observed by WhatsUp Gold in platform logs.
Notifications
- . Activate a beeper with this type of action.
- . Send an Email to a specific address.
- . Write a message to a text file.
- . Send a message to a pager.
- . Activate a Web Alarm in the WhatsUp Gold Web Interface
- . Plays a voice message on your computer.
- . Send a text message to a specific target.
- . Send a text message to a wireless phone or other wireless device.
- . Play a specific sound.
Remote/Local Script or Execution
- . Start or stop a Windows service.
- . Write code to perform a customized action.
- . Perform script or task from CM Task (includes Task Scripts) or CM Script Libraries.
- . Develop custom actions through direct access to scriptable component libraries, including the .NET Framework.
- . Connect to remote devices via SSH to execute commands or scripts.
- . Execute an external application.
- . Use SNMP to increase a counter, set a flag, or change the attribute value of a managed object.
Log
- . Write an event in the Windows Event Log.
- . Write a message to a log in the Syslog system.
- . Use the VMware API to perform an action on a virtual machine.
 Credentials. View and associate built-in credential types with this device. (Needed for rich discovery and monitoring information.) Credentials. View and associate built-in credential types with this device. (Needed for rich discovery and monitoring information.)
Credentials Library provides the following credential types:
. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv1, SNMPv2, SNMPv3).
Credential Type
|
Description
|
Typical Use
|
SNMPv1
SNMPv2
|
Administrative SNMP domains (for example, networks and subnets) are defined by a shared SNMP community string.
|
Poll with WhatsUp Gold performance monitors with access to MIBs on any device running an SNMP agent with a default ("public") or otherwise configured community string.
|
SNMPv3
|
User based security with SNMP message authentication for data integrity and origin authentication.
|
Poll with WhatsUp Gold Performance monitors for SNMP-enabled devices using SNMPv1,v2,v3.
- Ensure message privacy between a SNMPv3 agent and management station.
- Protect against MITM attacks due to replay.
|
. Windows, VMware, SSH (typically used for Linux and UNIX).
Credential Type
|
Description
|
Typical Use
|
WMI (Windows)
|
Windows user credentials. It is best practice to scope these according to the principal of least privilege.
|
|
SSH, Telnet (UNIX, Linux)
|
Remote commands, scripts, and management.
|
- Connect WhatsUp Gold to devices running an SSH Server.
- Access filesystem partition information on Linux, UNIX devices if not available by way of SNMP.
- Action scripts/Shell Scripts.
|
Telnet (UNIX, Linux)
|
Remote commands, scripts, and management.
|
- Connect WhatsUp Gold to devices running a Telnet Server.
- Shell access.
|
VMware
|
VM platform attributes, status, and logs.
|
- Needed to connect to vCenter server.
- Add to vCenter server.
- Enables VM and virtual server information to be gathered by way of VMware services.
|
. Secure Shell client (SSH), Telnet client.
Credential Type
|
Description
|
Typical Use
|
SSH
|
Remote commands, scripts, and management.
|
- Connect WhatsUp Gold to devices running an SSH Server.
- Access filesystem partition information on Linux, UNIX devices if not available by way of SNMP.
- Linux/UNIX/router switch CLI.
- Action scripts/shell scripts (SSH action, for example).
|
Telnet
|
Remote commands, scripts, and management.
|
- Connect WhatsUp Gold to devices running a Telnet Server.
- Shell access.
- Linux/UNIX/router switch CLI.
|
. Storage Management Initiative Specification (SMI-S).
. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure.
. ADO, JMX.
: Most active monitors that include scripting (PowerShell, for example) have the ability to apply credential sets as part of remote processing (before and during the active session).
Learn More
About Credentials.
Tips for Applying Credentials.
:: Most active monitors that include scripting (PowerShell, for example) have the ability to apply credential sets as part of remote processing (before and during the active session).
 Attributes. User-defined, role-defined, and other properties uncovered during discovery that describe the device. Attributes. User-defined, role-defined, and other properties uncovered during discovery that describe the device.
Attributes panel enables you to view device system and host descriptions, modify some of this information, and populate user defined attributes (such as Contact Information).
- Most fields are populated at discovery time such as device MAC address, device name, and so on. For example, for a Windows device, Discovery pulls in system and host information (Computer Properties) as attributes.
- Other fields, such as contact information, can be auto populated at discovery time using custom role definitions or edited through the Attributes panel.
: Attribute values can be auto populated using Device Role definitions. You can also customize Device Attributes using discovery percent variable syntax.
 Roles. Browse, apply, and template the model applied to this device for discovery, role determination, and default monitor scheme. Roles. Browse, apply, and template the model applied to this device for discovery, role determination, and default monitor scheme.
 Primary Role. Consider these roles as candidates for the current role definition during discovery/rescan. Primary Role. Consider these roles as candidates for the current role definition during discovery/rescan.
Select a generalized role class to apply.
Your role will inherit default characteristics from this class such as discovery attributes and default monitors that you can modify if appropriate.
 Sub Roles. Add sub roles to consider for discovery/rescan. Sub Roles. Add sub roles to consider for discovery/rescan.
Select a generalized sub role to apply (given your Scan Rules).
- .
 Add a monitor from the monitors library to this role definition. Add a monitor from the monitors library to this role definition. - .
 Remove a monitor from this list. Remove a monitor from this list.
Learn More
About Device Roles
: You can customize roles and subroles using the Roles/Subroles Editor.
 Inventory. (Information only) Tables of system-specific, host, OS, chassis and layer 2 connectivity and merge data reported by the selected device when discovered/rescanned. Inventory. (Information only) Tables of system-specific, host, OS, chassis and layer 2 connectivity and merge data reported by the selected device when discovered/rescanned.
Inventory provides complete views of the device management information.
- Richness of information depends on credentials available at scan time.
- Information available depends on device role/type. (Windows devices will show updates, switches show ARP cache, for example.)
- Information is read-only from this view.
- Discovery-time device boundary decisions and information used for merging determination.
 Refresh Timeline. Shows device history of add/update monitoring events and device rescan events. Refresh Timeline. Shows device history of add/update monitoring events and device rescan events.
- . Type of refresh that triggered the refresh.
- . Agent or task that triggered the refresh.
- . WhatsUp Gold User. (None for scheduled refresh/update actions.)
- . Date/time.
 Links. User-defined or role-associated URLs associated with the selected device. Links. User-defined or role-associated URLs associated with the selected device.
Define a custom link and apply it to the discovered device. You can customize for each device using discovery percent variable syntax.
- .
 Add a custom link. Add a custom link. - .
 Edit a selected custom link. Edit a selected custom link. - .
 Remove the link. Remove the link.
: Custom Links can be tabulated and distributed as Custom Link reports.
Examples
Add link for viewing web role or web service running on current device.
http://%Discovery.Device.Name.example.com:80
Add link to manage vCenter using vSphere web client.
https://%Discovery.Device.Name.example.com:9443/vsphere-client
 Applications. View and manage application instances WhatsUp Gold is monitoring on the selected device. Applications. View and manage application instances WhatsUp Gold is monitoring on the selected device.
Application Monitoring ( menu ) (also referred to as "APM") gathers performance statistics and overall application health while alerting on performance degradation and potential problems before they result in service outages. APM can assist organizations to measure service level and guarantee Service Level Agreements (SLAs) as well as assist in pinpointing application performance bottlenecks and points of failure. APM allows you to monitor the performance of "applications" and application-layer services running on your monitored devices.
Background
This section outlines the  essential building blocks you use to build your full APM solution. essential building blocks you use to build your full APM solution.
WhatsUp Gold and its supporting reference content use the following terminology when discussing application monitoring:
- . Groups application profiles, instances, and components by the type of application (e.g., Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft IIS, Microsoft Windows). After profiles, instances, and components are configured for an application, you will begin monitoring information about application health.
- . An application is made up of one or more programs running on one or more monitored systems. There are three distinct application types leveraged by WhatsUp Gold:
- . A simple application is an application that is not dependent on another application to run. Example: Microsoft Server 2008 R2.
- . A complex application is an application configured to be dependent on one or more applications to run (e.g., WhatsUp Gold requires IIS and SQL Server).
- . A discrete application is an application upon which a complex application has a dependency. (e.g., IIS and SQL Server are discrete applications on which the complex application WhatsUp Gold is dependent.) A discrete application is used when you are monitoring a complex application.
- . An application profile is a blueprint for monitoring a given type of application within WhatsUp Gold. It defines the collection of components and distinct applications that reflect the health and status of a specific type of application. An application instance is created from the application profile by associating it with the actual devices that host the components of the application as defined by the application profile. Changes to the application profile are inherited by all of the instances created from the profile. Changes in the profile are not inherited by overridden fields.
- . An application instance is a running copy of an application profile that monitors the defined collection of components, distinct applications, and thresholds necessary to define the health and performance of a given type of application. An application instance can extend the application profile by adding components, component groups, or discrete applications. The application profile is not changed when an application instance is extended.
- . A component is a single data point collected as part of an application profile (e.g., CPU Utilization)
- . A critical component is a component that impacts the status of an application instance. As a result, a critical component that goes into the down state, causes the application instance to go into the down state. However, if a non-critical component goes into a down state, the application instance goes into a warning state and only the component indicates being in the down state.
- . A critical component group is a grouping of components that contains specific logic to allow for complex evaluation of the up/down state of an application. For example, given four components A,B,C and D, the following logic can be applied, so that if A and B are down or C and D are down the application is placed into the down state. ((A and B) or (C and D)). Critical component groups are always considered "critical", in that if a critical component group is evaluated to be in the down state, the entire application is in the down state.
- Application Profile. Each monitored application is comprised of a collection of individual components as defined by an application profile.
- Application Instance. By applying an application profile to a monitored device, you instantiate an application monitoring instance ("Application Instance").
Discover
 Preparing to Discover. Select profiles you want applied during discovery or add new ones. Preparing to Discover. Select profiles you want applied during discovery or add new ones.
Configuring WhatsUp Gold to monitor an application is a simple process. It starts with selecting a profile that captures data points necessary to understand the performance, health, and status of a given type of application. The application profile groups the components, discrete applications, and associated thresholds necessary to capture the data points into a blueprint that can be used to create individual application instances. These instances actively monitor your applications. WhatsUp Gold provides a selection of profiles which are available upon successful WhatsUp Gold installation. You can also create your own application profiles. After you have the necessary profiles, you can automatically discover your applications and create instances for each discovered application, or you may choose to manually create and modify instances individually before you begin monitoring.
 Discovering Applications. Discover devices with resident applications that match selected application profiles. Discovering Applications. Discover devices with resident applications that match selected application profiles.
You can discover applications on and create application instances for devices monitored by WhatsUp Gold. To be discoverable, an application must have at least one discoverable service or process component associated with its profile. Ensure is enabled when adding or editing Windows service or process components within the application profile.
To discover applications:
- Select from the top navigation menu.
- Initiate application discovery by selecting one or more applications to discover, then click . Depending on your selection, this control is available within the and menus as well as at the top of the application grid. A navigation tree appears mirroring your device list which displays dynamic groups and discovery scans. Please note, if a dialog appears indicating one or more of the application profiles selected does not have discoverable components and will not be included in the search.", click .
- Select the groups and/or devices for which you want to discover applications by clicking the applicable check boxes in the navigation tree.
- Click . The Application Discovery: Discovery Results page appears.
After applications are discovered, use the list of newly discovered applications to select which ones to monitor and subsequently create application instances.
To monitor newly-discovered applications:
- Identify an application on the list you want to begin monitoring and click . A Start Monitoring Application dialog appears and WhatsUp Gold automatically begins testing the application profile components.
- Use the Start Monitoring Application dialog to make any desired changes to the instance you are creating. The dialog contains the following information:
- . Use this box to modify the default name of the application instance.
- . Use this list to select an action policy to be applied to the application instance.
- . Use this box to indicate how long a component test should run prior to timeout.
- . Use this button to immediately initiate component testing.
- . Use these check boxes to enable or disable individual components for the Application instance.
- . Use this box to indicate when WhatsUp Gold reports the component is experiencing a problem.
- . Use this box to indicate when WhatsUp Gold reports the component as 'Down'.
- Click to save the application instance.
- Close the dialog to return to the Application Discovery: Discovery Results page.
- Repeat these procedures as needed to create additional application instances.
Manage/Add Profiles/Monitor
You manage application instances by way of the Application and Profile Setup view ( menu ).
- Working with Application Profiles. Using built-in profiles, importing from WUGspace, and creating your own.
- Working with Application Instances. Managing deployed application monitors.
- Working with Components and Groups. Select data values to be monitored/sampled.
- Working with Discrete Applications. Monitoring underlying platforms for applications.
- Applying Actions and Action Policies. Apply state transition rules and corrective actions.
- Working with Application-Specific Attributes. Manage application descriptive data.
Analyze (dashboard, log, and report)
Analyze log, reporting, and dashboard data to assess performance, quality of service, and impact.
- Application Monitoring Dashboard. View, filter, and share application monitoring availability and performance.
- Application Event Log. Shows application events, actions, and state changes.
- Applications State Change Log. Shows transitions in application monitor states.
Capture/share/export
Application monitoring data can be visualized, shared, and reused using Export Data ( ) and Dashboard Options ( ) and Dashboard Options ( ). ).
 Tasks. Manage and run scheduled Configuration Management tasks as well as modify and compare archived configuration records assigned to the selected device. Tasks. Manage and run scheduled Configuration Management tasks as well as modify and compare archived configuration records assigned to the selected device.
Tasks enable you to apply controls, perform maintenance, and simulate user behavior, based on your site policies and goals.
Learn More
Typical Tasks
: For more details on how to build Scheduled Tasks and Password Tasks, see the section titled Configuration Management.
|
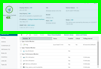
![]() Device Properties Panel
Device Properties Panel![]() ) is the central management/information point for any single managed device. It's the interface you leverage when bulk operations or group information (report data, for example) are not appropriate for your management task. Use Device Properties to apply changes, troubleshoot, and check configuration properties for any single device.
) is the central management/information point for any single managed device. It's the interface you leverage when bulk operations or group information (report data, for example) are not appropriate for your management task. Use Device Properties to apply changes, troubleshoot, and check configuration properties for any single device. 
 Device Configuration
Device Configuration